Everyone is waking up to the fact that estimates of what is possible in the economy are way off: this paper explains why
Potential output, generally understood as the highest level of output that may be attained without putting inflationary pressures upon the economy, is a crucial notion in the current design and management of macroeconomic policies. Empirical measures of this notion and of the distance between it and actual output—the so-called output gap—play a fundamental role in determining the expansionary or contractionary stance of both monetary and fiscal policy, and the margins for their use.
Mainstream economic theory sees potential output as determined exclusively by supply forces (essentially, resources and productivity), leaving to aggregate demand only the role of causing temporary deviations from it—precisely, the output gaps. When the economy is believed to be already operating at potential or slightly above, any increase in demand is regarded as dangerous for its dreaded inflationary consequences, and restrictive measures—such as the central bank raising interest rates—are taken.
Projections of the growth of potential output, in the longer term, are informative on the growth prospects of an economy. Since the Great Recession, a marked deterioration in potential growth is observable in virtually all available empirical estimates. Figure 1 shows, as an example, the downgrading of the Congressional Budget Office’s current estimates of US potential real GDP compared to the 10-year projections of January 2008.
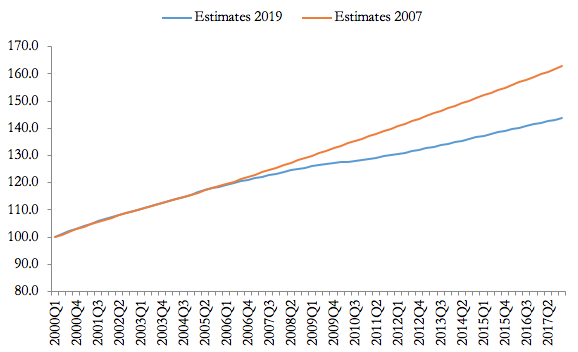
Figure 1: CBO’s potential output estimates and projections, 2000-2017 (2000Q1=100). Source: our elaboration on Congressional Budget Office estimates
That this is the effect of the crisis cannot be denied, both because the series of subsequent downward revisions in estimates started exactly in the wake of the Great Recession (Krugman, 2018), and because the greatest losses of potential output have occurred in those economies hit hardest by the crisis (Ball, 2014; Fatás, 2018). But the very fact that a downturn in demand, however deep, has affected potential growth is a challenge to deep-rooted theoretical beliefs—and opens the way to interpreting the question from a different theoretical perspective, in which demand is actually a major force in determining the long-run path of the system (Girardi et al., 2017; Storm, 2017), an idea long supported by the authors who proposed the notion of hysteresis (Blanchard et al., 2015).
A different theoretical perspective, however, also allows—indeed, requires—a reconsideration of both the very notion of potential output and its measures. Should we continue to define potential output as corresponding to a mythical non-accelerating-inflation rate of unemployment, supposedly the only rate at which inflation is stable, when empirical evidence clearly shows the absence of any regular short-run trade-off between inflation and unemployment—and we witness remarkable reductions in unemployment with virtually no effects on inflation? Evidence has posed so many challenges to the notion that Solow (2018, p. 423) has recently asserted that “there is no well-defined natural rate of unemployment, either statistically or conceptually.”
But how should potential output be defined if the mainstream definition is rejected? As for conventional measures, it is clear that standard estimation methods are unsatisfactory, given that they essentially boil down to calculating potential output as some sort of moving average of actual output. This presumes what needs to be shown: that the economy spontaneously converges towards equilibrium, so that actual output can never diverge too much from potential. The unobservable potential output, in other words, is always sought for in the vicinity of the realized one, which explains why the Great Recession, having produced negative effects on the actual trend of growth, also has affected potential output estimates. The procedure implies that no very big output gaps tend to open up, even in deep recessions, due to downward revisions in potential output estimates. This is much more than an academic issue, given the relevance of output gap measures for economic policy. Small estimated gaps imply in fact, consistent with the mainstream policy attitude, less need for and less scope for expansionary demand policies—and have more than once forced contractionary policies on already ailing economies, as for example with Southern European countries during the 2010s (Costantini, 2018).
It is clear then that new estimation methods, based on a theoretical re-consideration of the notion, are badly needed. In a recent INET working paper (Fontanari, Palumbo, Salvatori, 2019) we take up these questions. We propose to banish altogether the NAIRU ghost in potential output’s definition and measurement. Theoretically, potential output should be regarded, in our view, as the output that could be produced at full employment, so as to truly represent the extent of the production possibilities of an economy, and to allow for actual output to considerably deviate from it in cases of deep recessions.
Empirically, we propose in our paper an updated version of the method originally proposed by Arthur M. Okun in the 1960s. Compared to those currently in use in national and international institutions, the method has the distinct advantage of being entirely independent of the NAIRU and inflation data, since it is rooted in a ‘target’ rate of unemployment.
Okun’s (1962) procedure was aimed at answering the question “how much output can the economy produce under conditions of full employment,” and was closely related to the full-employment policies that were pursued by the US administration in those years. It is thus not only immune to some of the most obvious limitations of standard estimation methods, but also more consistent with our theoretical premises, i.e. with the idea that both actual and potential output can be affected by the evolution of aggregate demand.
On this basis, after re-estimating Okun’s law on US quarterly data on the 1959-2018 period, we obtain, through our Updated Okun Method (UOM), estimates of the US potential output and output gaps. Our estimates differ significantly from those produced by institutional agencies like the Congressional Budget Office, as shown in Figure 2 (where our estimated output gaps are obtained for the target rate of unemployment of 3.4 percent, the historical minimum of our sample. See the paper for details).
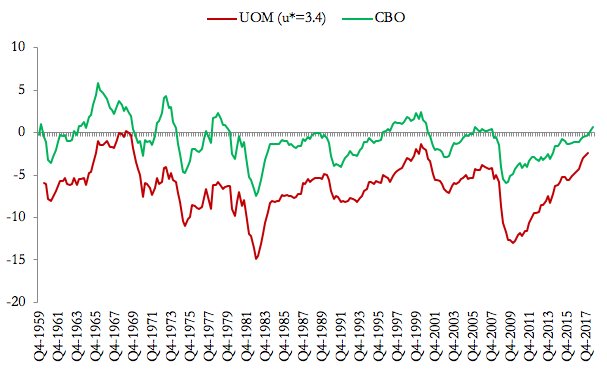
Figure 2: Output gaps obtained through the Updated Okun method (UOM) compared to those estimated by the CBO (USA, 1959-2017) Source: Fontanari, Palumbo, Salvatori (2019)
While the output gaps estimated by the CBO tend to fluctuate quite symmetrically around zero, our estimated output gaps are bigger in size and always negative. This is consistent with our definition of potential output as an upper ceiling rather than the average trend of actual output.
No methods, ours included, are immune to arbitrary assumptions and discretionary judgement, so that we cannot claim to have found the “true” measures of output gaps. Yet we believe that our method has a distinct advantage over standard estimation methods. Instead of defining potential output as the stochastic trend of actual output, thus assuming—but not proving—that the two can never diverge too much, it tries, though imperfectly, to identify and measure full-employment output, thus showing how far off the economy may be from its target and how wide are, in most circumstances, the margins for output expansion.
If our measures have limitations, indeed, they may lie especially in the fact that they tend to underestimate systematically such margins for output expansion. This for two reasons. In the first place, Okun’s procedure rests on the assumption that the rate of unemployment is a reliable indicator of labor and capacity underutilization: this might be questionable, especially in some particular historical phases, such as, for example, the one the American economy is experiencing. On the hypothesis that the current very low rates of unemployment in the USA do not imply that the economy is actually at full employment (or even beyond) but rather mask some relevant underutilization of labor, the use of official unemployment data in our procedure would imply serious underestimation of potential output in the last part of the sample.
Secondly, and more importantly, Okun’s (and thus our) measure defines potential output as the level of output that would have been produced if, in any given situation, installed capacity were fully utilized. What this notion of potential does not consider are the possible effects of the actual level and growth of output on the future potential path of growth, thanks to the ways aggregate demand affects the very creation of capacity and may influence the velocity of adoption of technical innovations. We thus attempt to push the analysis a step further and try to estimate, albeit approximately, the long-period path of growth that the economy would have followed if aggregate demand had been persistently strong enough so as to produce unemployment rates always near target, taking into account the effects of such high demand on the growth of productive forces. We simulate such a hypothetical path of growth by projecting over the whole time span the historically observed growth of ‘supply factors’ (labor force, hours per employed person, and productivity) in two benchmark periods, identified as those periods in which growth of demand was strongest.
Differently from the measures based on the Updated Okun Method, this simulated potential path (that we label the ‘high-demand potential path”) shows at a certain date what the economy would have been able to produce if the growth of productive forces had been fostered, over a long period in the past, by persistently strong demand. Figure 3 compares our two different notions of potential output with actual output.
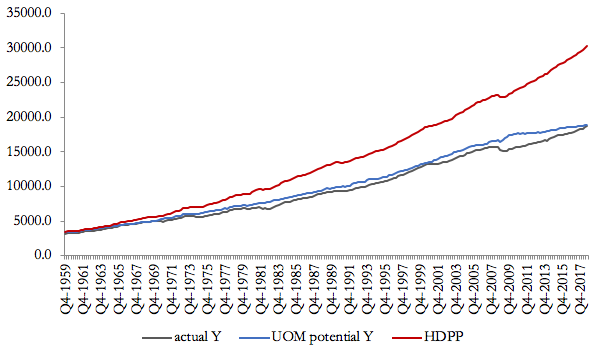
Figure 3: A comparison between actual output, UOM potential output and the High-Demand Potential Path (u*=3.4) Source: Fontanari, Palumbo, Salvatori (2019)
The high-demand potential path shows how far the sluggish growth of actual demand in some periods in the sample has prevented potential output (the blue line) to grow as much as it could. Not only do recessions open up big gaps between actual and potential output, as our UOM potential shows, but all phases of stagnating or slowly growing demand make the pace of resource accumulation and productivity growth slow down, thus causing a downward displacement of the whole long-run path of potential output.
The existence of such wide margins for potential output growth does not imply, of course, that they may be actually exploited entirely in a single period. But it implies that a determined policy of demand expansion would create, given time, the very capacity that justifies it—also re-absorbing inflationary pressures that might materialize in the short period. Policy discussions should focus on what kind of demand expansion is more conducive to long-period growth and what kind of supply measures should accompany it in order to avoid imbalances and prevent undesirable side effects.
If standard estimates tend to completely overlook the margins for output expansion—offering the spectacle of repeated revisions in an anxious chase of ever-surprising reality—and policy discussions focus too often on the need for restriction, this rests entirely with the questionable theoretical foundations of the very conception of potential output embraced in mainstream economics. The demand-led growth perspective both allows a conceptual reconsideration and redefinition of the notion, and implies a very different view of policy.
Just as an economy that has undergone deep recessions and long periods of slow growth has slowed down the pace of creation of its capacity or even destroyed part of it, thereby reducing its own growth prospects, so can it respond positively to a lasting expansion in demand and develop its capacities beyond the limits that now seem insurmountable.
References
Ball, L. M. (2014). Long-term damage from the Great Recession in OECD countries, (No. w20185). National Bureau of Economic Research.
Blanchard, O. J., Cerutti, E. M., Summers, L. (2015). Inflation and Activity–Two Explorations and their Monetary Policy Implications. International Monetary Fund (No. 15/230).
Costantini, O. (2018). Why Hysteria Over the Italian Budget Is Wrong-Headed. Institute for New Economic Thinking Blog, available at https://www.ineteconomics.org/…
Fatás, A. (2018). Fiscal policy, potential output and the shifting goalposts. CEPR Discussion Paper No. DP13149
Girardi, D., Paternesi Meloni, W., Stirati, A. (2017). Persistent Effects of Autonomous Demand Expansions. Institute for New Economic Thinking, Working Paper No. 70, available at https://www.ineteconomics.org/…
Krugman, P. (2018), The Economic Future Isn’t What It Used to Be (Wonkish), The New York Times, available at
https://www.nytimes.com/2018/0…
Solow, R. (2018). A theory is a sometime thing. Review of Keynesian Economics, 6(4), 421-424.
Storm, S. (2017). The New Normal: Demand, Secular Stagnation and the Vanishing Middle-Class. Institute for New Economic Thinking Blog, Working Paper No. 55, available at https://www.ineteconomics.org/…